- Opening Hours: 10am to 7pm(Monday-Saturday). Sunday on call appointment
- +91-9958309690, 8586929155 Book Appointment
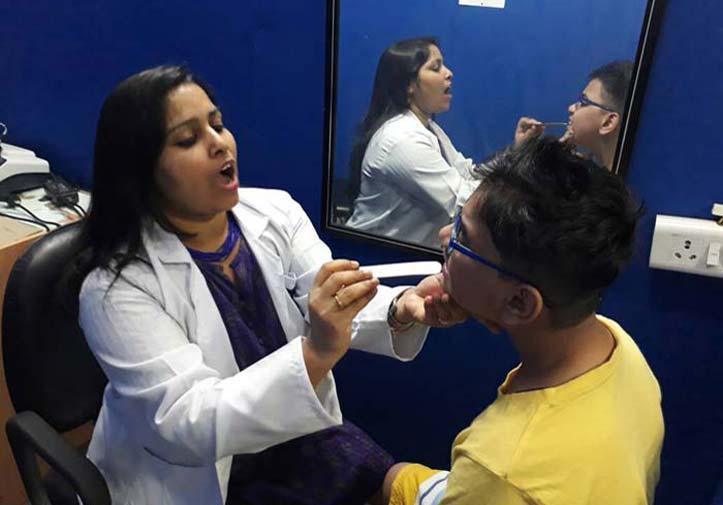
Stammering, which is also known as childhood-onset fluency disorder is a form of speech disorder that is characterized by stammering or dysfluent speech. Dysfluency is characterized by interruptions to speech flow. Stutterers may have trouble repeating words and the syllables. They might also exhibit an unbalanced pace of speech, which is reflected by frequent pauses or delays.
Stuttering is a common problem in children between 2 and 6. It usually disappears on its own. However, there are some who be affected by the condition for the rest of their lives. There are many effective methods to assist people in overcoming the stutter, and also strategies to improve speech efficiency.
Childhood fluency disorder affects 5-10 percent of preschoolers and about 1percent of adults.
Signs and symptoms of StammeringStammering can be described as dysfluent speech that has the overt and the covert (hidden) symptoms. Some examples of this include repeated sounds, difficulty in speaking certain words, or struggling to begin a word or sentence.
Overt signs are evident to others and can include:
Alongside the symptoms of speech Stammering can also be associated with "struggle behavior." The people who stutter are aware of what they would like to say, however they are unable to speak the words to come out in an orderly flow. If they are struggling in their communication, they may show blinks, quick eye movement, facial tremors and other facial expressions.
Other examples of stress-related behavior that can occur while trying to communicate include:
Stuttering may also cause feelings of shame in social settings. If you struggle with your speech and you are embarrassed, you might feel anxiety, stress, avoidance, low self-esteem issues, and depression.
Reasons
The causes for stuttering aren't clear however; it is possible that it has an underlying genetic cause, as it is sometimes seen within families. Other possible causes and contributing factors are:
Stuttering can also occur in people who are suffering from an extreme amount of emotional stress. For instance, those suffering from social anxiety disorder (SAD) might occasionally stutter in stressful social settings.
Stutterers may feel anxious when they are in social situations, it is not a sign that they suffer from social anxiety disorder. If you're only worried because you stutter, then you won't be classified as having SAD since the anxiety is primarily about stuttering and not performance or social situations.
Treatment
There isn't a solution to stuttering but there are many methods that can aid. Stammering treatment in Noida typically focuses on helping adults and children improve their skills, such as communication, active participation at work and in school and fluency in speech. In order to achieve the goals set, there is a range of stammering treatments in Delhi that can be utilized, including:
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT): A form of therapy is a way to help individuals recognize and alter the kind of thinking which can cause stuttering more difficult. For instance, negative thoughts could cause people to feel increased stress and anxiety which can make it more difficult to stutter in certain circumstances. CBT can be beneficial to address the symptoms of anxiety, low self-esteem and depression and social anxiety disorders.
Electronic gadgets: There exist a variety of kinds of electronic wearable devices that can help in the treatment of stuttering. However, more studies are needed to establish how effective they are. They are worn as hearing aids. They can play background music while others prompt the wearer to speak slowly.
Speech therapy: In speech therapy, patients collaborate with a speech therapist to find ways to lessen the amount of stuttering. Strategies like regulating breathing and speaking slow for instance, will frequently help. Speech therapy can make people feel less nervous when speaking.
While medications like selective serotonin receptor inhibitors (SSRIs) have been found to be effective in treating co-occurring disorders like depression or social anxiety disorder but there isn't enough research to prove their use in the treatment of stuttering.
 Healthy habits to take care of your voice.
Healthy habits to take care of your voice.
 Tips To Follow To Help You Stop Stuttering or Stammering
Tips To Follow To Help You Stop Stuttering or Stammering
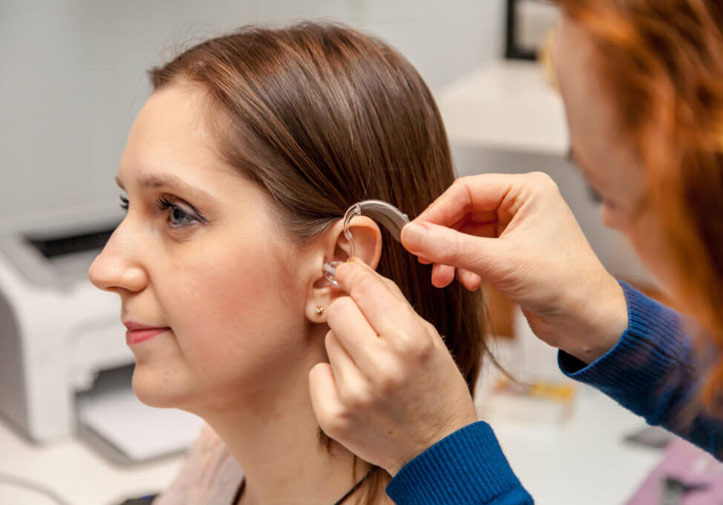 Getting used to new hearing aids
Getting used to new hearing aids
 When should we replace your hearing aids?
When should we replace your hearing aids?
 What Are Hearing Aids?
What Are Hearing Aids?
 Know More About Neurological Stroke Language Disorders!
Know More About Neurological Stroke Language Disorders!
 Advanvement of Technology In Digital Hearing Aids!
Advanvement of Technology In Digital Hearing Aids!
 Autistic Children - How Can Speech Therapy Assist?
Autistic Children - How Can Speech Therapy Assist?
 Stammering - Know About Its Cause And Treatment!
Stammering - Know About Its Cause And Treatment!
 How Speech Therapy Can Help Your Child?
How Speech Therapy Can Help Your Child?